Wireshark allows you to trace all of the packets received and sent by your NIC. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting configuration issues with your carrier and with the Voice Elements Platform.
For more information about Wireshark, please visit their website or read more in this Wikipedia article.
Download Wireshark
Wireshark is an open source software product that can be downloaded from Wireshark.org.
Setting up a trace in Wireshark
Once you have downloaded and installed Wireshark, you may begin tracing network traffic. To do this you must first open Wireshark, and select a network interface. Below is an image that displays how to do this (See the highlighted button):
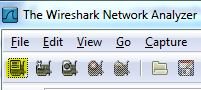
Next, Wireshark will display a list of network interfaces, like the image below:
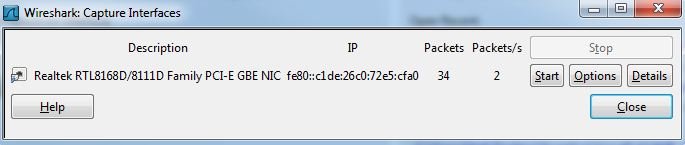
If you have more than one NIC, it’s important to select the correct one. You may begin your trace, by clicking the start button.
Once the trace has begun, you will begin seeing networking traffic. Each individual line represents a TCP or UDP packet.
Stopping your Wireshark trace
You may stop your Wireshark trace, by selecting the stop, button. Please refer to the image below:
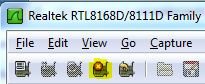
Saving your Wireshark trace
Once you have stopped your trace. You may save the resultant file as a .PCAP file, by going to “File” > “Save As”.
You may then select a file location and filename.
Advanced Topics
Listening to Audio from a call
If you have recorded all of the SIP and RTP packets on a call, you can use Wireshark to listen to the audio of a call. To do this, you will need to browse to “Telephony > Voip Calls”. You should then see a list of all of the SIP sessions that were established since you began the trace. You can then select a call, and click “Player” to listen to the audio.
Below is an image that shows this feature:
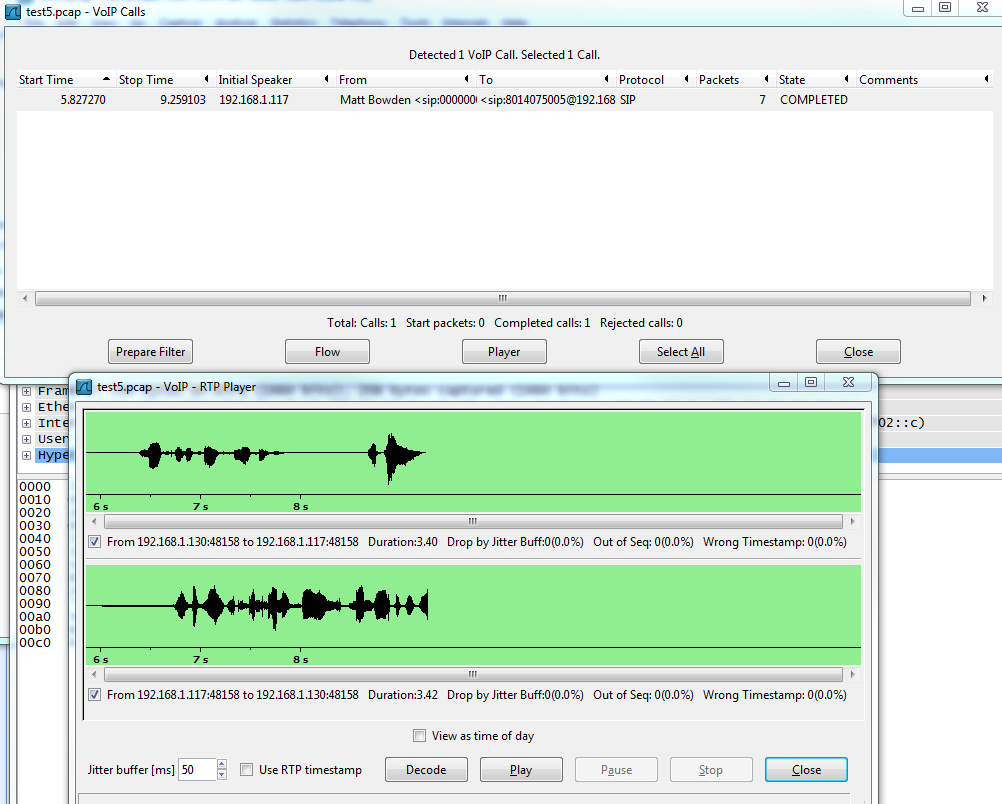
Capture Filters
These are useful for cutting down the amount of traffic that is being traced.
http://wiki.wireshark.org/CaptureFilters
Display Filters
These are useful for cutting down the amount of traffic that is displayed. This can come in handy when troubleshooting an issue as it is occurring. For example, you may enter a filter of “SIP” to display just the SIP packets that are being sent and received by your NIC.
http://wiki.wireshark.org/DisplayFilters
